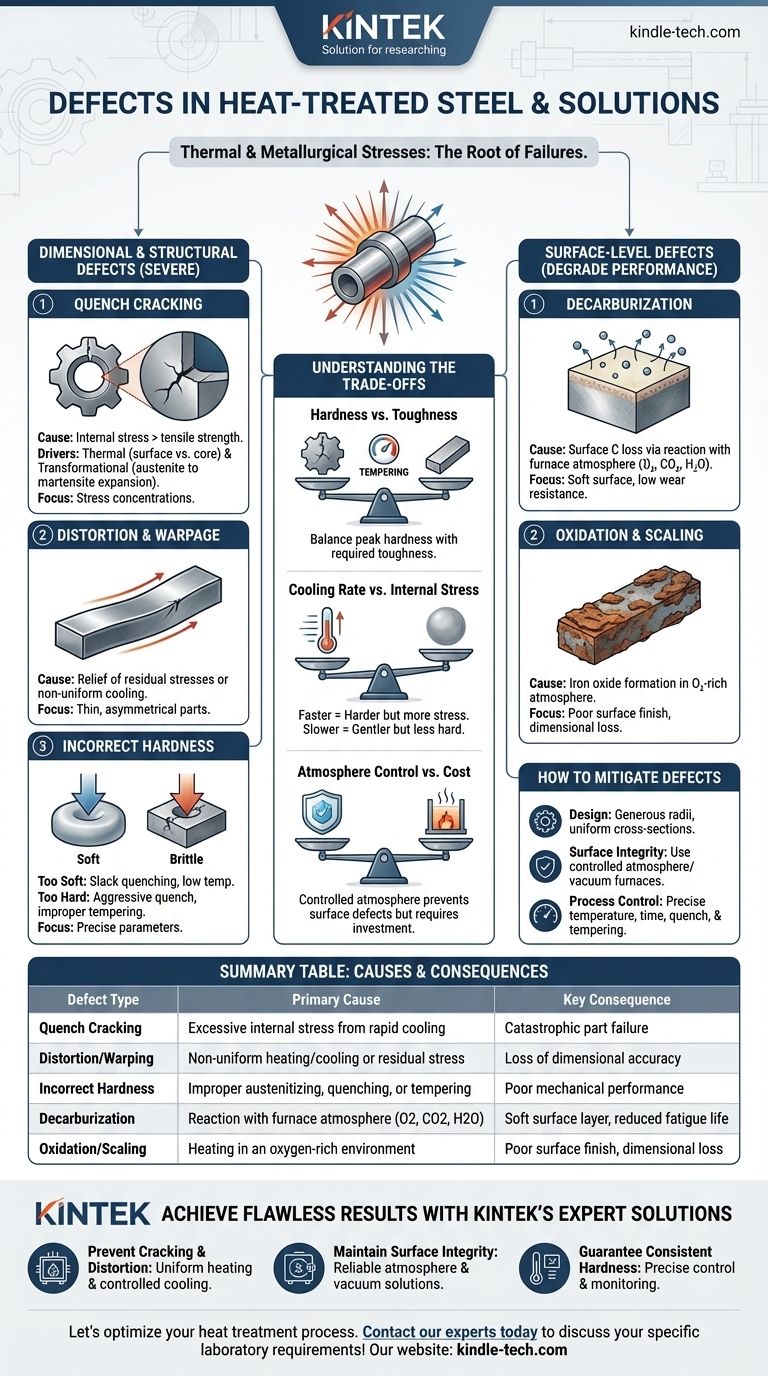
열처리된 강철의 결함은 주로 가열 및 급속 냉각 중에 발생하는 엄청난 열적 및 야금학적 응력으로 인해 발생합니다. 가장 흔한 결함은 균열, 변형(뒤틀림), 탈탄 및 스케일링과 같은 바람직하지 않은 표면 변화, 그리고 목표 경도 또는 미세 구조를 달성하지 못하는 것입니다. 이러한 실패는 무작위가 아니라 부적절하게 제어된 공정 매개변수의 직접적인 결과입니다.
열처리 결함은 열 응력, 상 변태 및 대기 화학 반응의 예측 가능한 결과입니다. 이를 방지하는 것은 온도 변화 속도, 용광로 분위기 및 설계 단계부터 부품의 형상을 엄격하게 제어하는 데 달려 있습니다.

치수 및 구조적 결함
가장 심각한 결함은 부품의 기계적 무결성과 치수 정확도를 손상시켜 종종 사용 불가능하게 만듭니다.
급랭 균열
급랭 균열은 가장 치명적인 열처리 결함입니다. 이는 급랭 중 내부 응력이 재료의 극한 인장 강도를 초과할 때 발생합니다.
이는 두 가지 주요 힘에 의해 발생합니다: 표면이 코어보다 훨씬 빠르게 냉각될 때 발생하는 열 응력과 오스테나이트가 취성 마르텐사이트로 변태할 때 발생하는 팽창으로 인한 변태 응력입니다.
균열은 일반적으로 날카로운 모서리, 키홈 또는 부품 단면의 급격한 변화와 같은 응력 집중 지점에서 발생합니다.
변형 및 뒤틀림
변형은 열처리 중에 발생하는 부품의 크기 또는 모양의 돌이킬 수 없는 변화입니다.
이는 종종 이전 제조 단계(예: 기계 가공)에서 발생한 잔류 응력의 해소 또는 불균일한 가열 및 냉각으로 인해 발생합니다. 얇고 길거나 비대칭적인 부품은 특히 뒤틀림에 취약합니다.
부정확한 경도
정확한 경도를 달성하는 것이 종종 주요 목표이며, 여기서의 실패는 여러 요인으로 인해 발생할 수 있습니다.
너무 부드러운 부품은 불충분한 오스테나이트화 온도 또는 시간, 또는 강철의 경화능에 비해 너무 느린 급랭(슬랙 퀜칭으로 알려짐)으로 인해 발생할 수 있습니다.
반대로, 너무 단단하고 취성 있는 부품은 종종 지나치게 공격적인 급랭 또는 더 일반적으로 경화 후 부적절하거나 누락된 템퍼링 단계의 결과입니다.
표면 수준 결함
이러한 결함은 강철 표면을 손상시켜 높은 내마모성 또는 피로 강도가 필요한 응용 분야에서 성능을 저하시킵니다.
탈탄
탈탄은 강철 표면에서 탄소가 손실되는 현상입니다. 탄소는 강철의 경도를 담당하는 주요 원소이므로 이는 중요한 문제입니다.
이는 고온에서 강철과 용광로 분위기(산소, 이산화탄소, 수증기) 사이의 화학 반응으로 인해 발생합니다. 그 결과는 내마모성 및 피로 수명을 크게 감소시키는 부드럽고 약한 표면층입니다.
산화 및 스케일링
산화는 산소가 풍부한 분위기에서 가열될 때 부품 표면에 산화철(스케일) 층이 형성되는 것입니다.
이 스케일은 표면 조도를 저하시키고 치수 정확도를 손실시킵니다. 또한 부품을 단열하여 불균일한 급랭을 유발하고 급랭 균열과 같은 더 심각한 근본적인 결함을 가릴 수 있습니다.
절충점 이해
열처리 공정을 선택하는 것은 항상 상충되는 요인들의 균형을 맞추는 것을 포함합니다. 이러한 절충점을 이해하는 것이 결함을 방지하는 핵심입니다.
경도 vs. 인성
열처리에서 근본적인 절충점은 급랭과 같이 극도의 경도를 생성하는 공정이 취성 미세 구조(비템퍼링 마르텐사이트)도 생성한다는 것입니다.
템퍼링은 이러한 취성과 내부 응력을 줄여 인성을 부여하는 필수적인 급랭 후 단계입니다. 그러나 이 과정은 또한 최대 경도를 감소시킵니다. 핵심은 응용 분야에 필요한 정확한 균형을 찾는 것입니다.
냉각 속도 vs. 내부 응력
더 빠른 냉각 속도는 특히 저합금강에서 완전한 경도를 달성하는 데 더 효과적입니다.
그러나 급속 급랭(예: 물 또는 염수 사용)은 엄청난 열 구배와 내부 응력을 발생시켜 변형 및 균열 위험을 극적으로 증가시킵니다. 더 느린 급랭(예: 오일 또는 가스 사용)은 더 부드럽지만 최대 경도를 달성하지 못할 수 있습니다.
분위기 제어 vs. 비용
제어된 분위기(예: 진공, 질소 또는 아르곤)를 사용하면 탈탄 및 산화를 완전히 방지하여 깨끗하고 밝은 부품을 얻을 수 있습니다.
그러나 이러한 공정은 개방형 용광로에서 가열하는 것에 비해 더 정교하고 비싼 장비가 필요합니다. 비용은 부품의 표면 요구 사항에 따라 정당화되어야 합니다.
열처리 결함 완화 방법
결함을 방지하려면 설계, 재료 선택 및 정밀한 공정 제어에 중점을 둔 체계적인 접근 방식이 필요합니다.
- 균열 및 변형 방지에 중점을 둔다면: 넓은 반경과 균일한 단면을 가진 부품을 설계하고 강철의 경화능에 적합한 덜 가혹한 급랭 매체를 선택하십시오.
- 표면 무결성 유지에 중점을 둔다면: 제어된 분위기 용광로(예: 진공, 불활성 가스) 또는 보호 코팅을 사용하여 탈탄 및 스케일링을 방지하십시오.
- 일관된 경도 달성에 중점을 둔다면: 오스테나이트화 온도, 유지 시간 및 급랭 교반을 정밀하게 제어하고 항상 적절한 템퍼링 사이클을 따르십시오.
성공적인 열처리는 설계의 선견지명과 실행의 정밀도가 부품의 최종 품질을 결정하는 제어된 엔지니어링 공정입니다.
요약 표:
| 결함 유형 | 주요 원인 | 주요 결과 |
|---|---|---|
| 급랭 균열 | 급속 냉각으로 인한 과도한 내부 응력 | 치명적인 부품 고장 |
| 변형/뒤틀림 | 불균일한 가열/냉각 또는 잔류 응력 | 치수 정확도 손실 |
| 부정확한 경도 | 부적절한 오스테나이트화, 급랭 또는 템퍼링 | 불량한 기계적 성능 |
| 탈탄 | 용광로 분위기(O2, CO2, H2O)와의 반응 | 부드러운 표면층, 피로 수명 감소 |
| 산화/스케일링 | 산소가 풍부한 환경에서 가열 | 불량한 표면 조도, 치수 손실 |
KINTEK의 전문가 솔루션으로 완벽한 결과 달성
비용이 많이 드는 열처리 결함을 제거하고 강철 부품이 경도, 내구성 및 치수 정확도에 대한 최고 표준을 충족하도록 보장하십시오. KINTEK은 프리미엄 실험실 장비 및 소모품을 전문으로 하며, 실험실이 열처리를 완벽하게 하는 데 필요한 정밀한 용광로, 분위기 제어 시스템 및 전문가 지원을 제공합니다.
우리는 다음을 돕습니다:
- 균열 및 변형 방지: 균일한 가열 및 제어된 냉각을 위해 설계된 장비로.
- 표면 무결성 유지: 신뢰할 수 있는 분위기 제어 및 진공 용광로 솔루션을 통해.
- 일관된 경도 보장: 정밀한 온도 제어 및 모니터링 도구로.
열처리 공정을 최적화합시다. 지금 전문가에게 문의하여 특정 실험실 요구 사항에 대해 논의하십시오!
시각적 가이드